CONSULTING AND ADVISORY
ONLINE WORKSHOPS
1- Reservoir Management and Surveillance:
Surveillance tools and methods to monitor reservoir and well performance.
- Information resources for monitoring current well and field performance in oil/gas reservoirs. Reservoir surveillance data collection upon well field, reservoir conditions and production data.
- Analytical methods and models used to characterize oil/gas reservoirs performance, surveillance and management.
- Evaluation of information related to rock and fluid sampling, well testing, cased hole formation evaluation, production logging, pressure surveys ad so forth in order to facilitate control of reservoir performance,
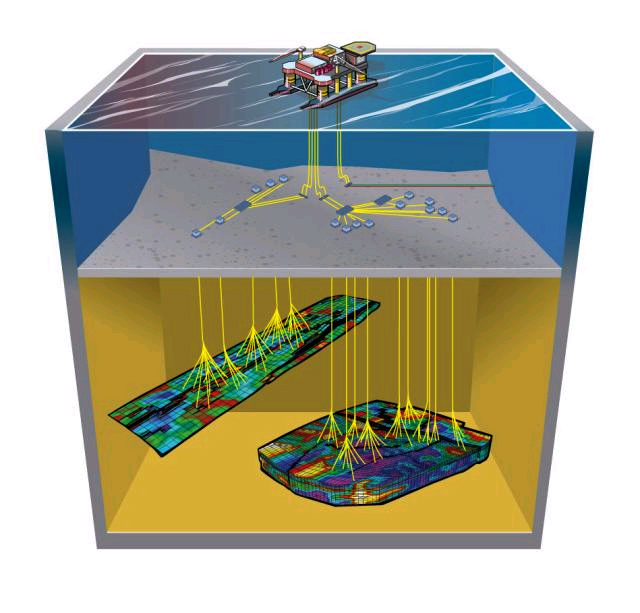
Surveillance tools and methods to monitor reservoir and well performance.
Justify development expenditures while maximizing benefits.
•Tools and methods used to generate the current forecasts (Crystal Ball, choke model, decline curve analysis).
• Workflows related to field development planning.
• Role of production forecasting in optimizing asset development.
• Impacts of reservoir drive mechanisms, well inflow performance and surface production operations on the production performance forecasting
• Forecasting tools (analytical methods, simulation, analogues, etc.) to generate forecast variants for current forecast.
For use in financial reporting on the SEC, SPE and other regulatory bodies.
- Classify reserves as proved, unproved probable or possible based on SPE-WPC definitions.
- Reserves status categories (developed, producing, non-producing and undeveloped) as defined by SPE-WPC.
- Methodologies for reserves estimation and reporting (SEC, SPE/WPC).
- Features, areas of application and limitations of commonly used reserves calculation methods (analogy, volumetric, material balance, decline curve analysis and reservoir simulation).
- Probabilistic reserves estimation methods applicability, assumptions, limitations, differences and pros/cons versus deterministic methods.
Reservoir geometry, reservoir properties and fluid properties on natural drive mechanisms.
• Natural drive mechanisms in oil and gas reservoirs.
• Field and laboratory data requirements for material balance applications.
• Interpret material balance plots. Apply material balance methodologies to identify natural drive mechanisms..
• Predict reservoir performance using material balance methodologies.
5. Reservoir Well Testing Design and Analysis:
Individual well and reservoir performance through design and execution of well testing.
- Reservoir parameters that may be derived from a properly designed well test, as well as the limitations inherent in well test analysis.
- Effects of reservoir anisotropy and heterogeneity on well testing response.
- Interpretation methods for pressure transient tests: Conventional (Horner plot) and advanced (pressure derivatives, types curves).
- Interpret well test results by integration with reservoir static information and properties.

Individual well and reservoir performance through design and execution of well testing.
• Laboratory tools and methods used to characterize the phase behavior of different reservoir fluid systems.
• Read and interpret results of a laboratory PVT analysis.
• Types of laboratory PVT rests that ae run on different types of hydrocarbon samples.
• Review and validate interpretations of laboratory PVT data.

Analysis using the appropriate software applications (well, reservoir and network field model) to optimize field performance and perform production forecasting.
- Production Network modeling and effect of fluids properties and system design on the overall system performance.
- Sensitivity analysis using production network model to identify production problems within the gathering system and wells.
- Integrate subsurface and surface models to perform production history matching and predict estimated production gain through integrated Production Modelling.
- Field production history matching by integration of surface, well and network modes and forecast production behavior.
Number, type and location of wells to be drilled to achieve production objectives.
• Optimal way to develop and produce from oil or gas fields that successfully manages risks uncertainty and value to stakeholders.
• Develop a Field Development Plan to provide the best technical solution and guide for optimizing the development and production of the field.
• Decide the best production/injection well placement and design, including surface facilities, economics and risk assessment.
